There are numerous practical applications of electrical laws in our daily lives. Here are some examples:
Ohm's Law: Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. One practical application of Ohm's Law is the use of resistors in electronic circuits to control the flow of current and voltage.
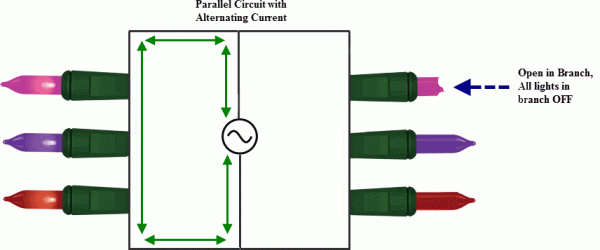
Kirchhoff's Laws: Kirchhoff's Laws are used to analyze complex electrical circuits. They are applied to calculate the current, voltage, and resistance values in circuits, and to determine the behavior of electrical components like capacitors and inductors.
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Law states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor. This law is used in the design of generators, transformers, and electric motors.
Coulomb's Law: Coulomb's Law describes the interaction between electrically charged particles. It is used to calculate the force between two charged particles, and to design capacitors and electrostatic precipitators.
Ampere's Law: Ampere's Law describes the relationship between electric current and magnetic fields. It is used in the design of electromagnets and magnetic storage devices like hard drives.
These are just a few examples of the practical applications of electrical laws. Electrical laws are fundamental to the functioning of a wide range of devices and systems, including power grids, electronic devices, and communication networks.
