Introduction:Enamelled wire, also known as magnet wire or winding wire, plays a crucial role in various electrical applications. It is widely used in motors, transformers, generators, and other devices that require a compact and efficient electrical conductor. In recent years, advancements in technology and materials have led to the development of a wide range of enamelled wires, each with unique characteristics and applications. In this blog, we will explore the top five types of enamelled wire that are revolutionizing the electrical industry in 2023.
Polyurethane (PU) Enamelled Wire:Polyurethane enamelled wire is one of the most commonly used types of enamelled wire due to its excellent electrical properties and affordability. It exhibits good thermal stability, high dielectric strength, and low friction, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Polyurethane enamelled wire is commonly found in small motors, transformers, solenoids, and relays.
There are different types of PU enamelled wires available, categorized based on their temperature rating and usage. Here are some common types:
Class 130/155: These PU enamelled wires are designed for general-purpose applications and have a temperature rating of 130°C continuous or 155°C intermittent. They are commonly used in motors, transformers, relays, and other electrical equipment.
Class 180: PU enamelled wires of this class have a higher temperature rating of 180°C continuous or 200°C intermittent. They offer improved thermal resistance and are suitable for applications that require higher operating temperatures, such as in motors, transformers, and generators. The
180°C Enameled Copper Wire is the better sales.
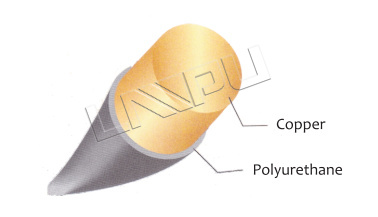
Class 200: These wires are designed to withstand higher temperatures, with a temperature rating of 200°C continuous or 220°C intermittent. They are commonly used in high-temperature applications like magnet wire for high-temperature coils and windings.
Self-bonding wires: Some PU enamelled wires are designed to have self-bonding properties, where the insulation material adheres to itself when heated. These wires are used in applications that require coil windings to be held in place without the need for additional adhesives or tapes.
Fine-gauge wires: PU enamelled wires are also available in fine gauges, suitable for applications requiring thin wire diameters. These wires find use in industries such as electronics, telecommunications, and miniaturized devices.
It's important to note that the specific types and temperature ratings of PU enamelled wires can vary among manufacturers, so it's always recommended to check the specifications provided by the wire manufacturer to ensure the wire's suitability for your intended application.
Polyamide-Imide (PAI) Enamelled Wire:Polyamide-imide enamelled wire offers exceptional thermal and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 220°C, making it suitable for use in harsh environments such as automotive applications, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Polyamide-imide enamelled wire exhibits excellent electrical performance, mechanical strength, and resistance to abrasion.
There are different types of PAI enamelled wire available, depending on their specific characteristics and applications. Here are a few common types:
Standard PAI Enamelled Wire: This type of PAI wire is the most commonly used and offers excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It is suitable for high-temperature applications and is often used in motors, transformers, and other electrical equipment.
Thermal Class H (200°C) PAI Enamelled Wire: This type of PAI wire is designed to withstand continuous operation at high temperatures up to 200°C. It has enhanced thermal resistance compared to standard PAI wire and is commonly used in applications where high-temperature stability is required. Go to see the
200°C PAI Enamelled Aluminum Wire.

Thermal Class C (220°C) PAI Enamelled Wire: This type of PAI wire is designed to operate at even higher temperatures, up to 220°C. It provides superior thermal stability and is suitable for demanding applications where exposure to elevated temperatures is expected.
Thermal Class F (155°C) PAI Enamelled Wire: Although not as heat resistant as the previous types, this PAI wire is still capable of withstanding temperatures up to 155°C. It is often used in applications where high-temperature resistance is necessary but not extreme, such as in certain types of motors and transformers.
Self-Bonding PAI Enamelled Wire: This type of PAI wire has a special coating that enables the wire to bond to itself when heated, eliminating the need for additional bonding agents or adhesives. It is commonly used in coil winding applications where securing the wire windings is required.
These are some of the common types of PAI enamelled wire available. The selection of the wire type depends on the specific application requirements, including operating temperature, electrical properties, and environmental conditions. It is important to consult the manufacturer or supplier to determine the most suitable type of PAI enamelled wire for a particular application.
Polyester (PE) Enamelled Wire:Polyester enamelled wire, also known as modified polyester wire, is known for its outstanding mechanical strength and durability. It offers excellent resistance to moisture, solvents, and chemicals, making it a preferred choice for applications in the automotive, electrical, and domestic appliance industries. Polyester enamelled wire is often used in coils, motors, ballasts, and household electrical equipment.
Polyester (PE) enameled wire is a type of magnet wire used in electrical and electronic applications. It is available in different types and classifications based on various factors. Here are some different types of polyester enameled wire:
.jpg)
Polyester Round Wire: This is the most common type of enameled wire with a round copper conductor and a polyester enamel insulation coating. It is widely used in general-purpose applications where moderate thermal resistance and electrical insulation are required.
Polyester Rectangular Wire: This type of enameled wire has a rectangular-shaped copper conductor and a polyester enamel insulation. It is commonly used in applications where space is limited, and the rectangular shape provides better utilization of available space.
Polyester Triple Insulated Wire: Triple insulated wire consists of multiple layers of polyester enamel insulation, providing enhanced electrical insulation properties. It is typically used in high-voltage applications where additional insulation layers are required for safety and performance.
Polyester Self-bonding Wire: This type of enameled wire has a self-bonding enamel coating that adheres to itself when heated. It eliminates the need for additional adhesive or tying during winding, making it suitable for applications where coil integrity is crucial.
Polyester Litz Wire: Litz wire consists of multiple strands of individually insulated magnet wire twisted together. Polyester enameled wire is used as the individual strand insulation in Litz wire, providing good electrical insulation and flexibility. About the
Litz Wire, you can see this blog.
Polyester Fiber Optic Wire: Polyester enameled wire is also used in fiber optic applications as a protective coating for fiber optic cables. It provides mechanical protection and helps maintain signal integrity.
These are some of the different types of polyester enameled wires available in the market. The specific type and specifications of the wire depend on the intended application, voltage requirements, temperature rating, and other factors.
Polyimide (PI) Enamelled Wire:Polyimide enamelled wire is highly regarded for its exceptional thermal stability and excellent electrical properties. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -200°C to 250°C, making it suitable for applications in extreme temperature environments such as aerospace, oil exploration, and high-temperature electrical equipment. Polyimide enamelled wire is also known for its high resistance to chemicals, radiation, and abrasion.

Polyimide (PI) enamelled wire is a type of magnet wire commonly used in applications that require high-temperature resistance, excellent electrical insulation, and good mechanical properties. Here are some different wire types of Polyimide (PI) enamelled wire:
Round Wire: This is the most common type of Polyimide enamelled wire. It is available in various diameters, and its circular cross-section makes it easy to wind and handle.
Rectangular Wire: Also known as flat wire, this type of Polyimide enamelled wire has a rectangular cross-section. It offers advantages such as increased packing density and improved heat dissipation compared to round wire. See the
200°C Polyimide Rectangular Aluminum Enamelled Wire.
Square Wire: Square Polyimide enamelled wire has a square cross-section. It combines the advantages of round and rectangular wire, providing improved space utilization and good thermal characteristics.
Litz Wire: Litz wire consists of multiple strands of Polyimide enamelled wire twisted or braided together. The individual strands are insulated from each other and offer reduced skin effect at high frequencies. Litz wire is commonly used in high-frequency applications and transformers.
Self-bonding Wire: Self-bonding Polyimide enamelled wire has a special adhesive coating that activates when heated. This allows the wire to bond to itself during winding, eliminating the need for additional securing methods.
Triple Insulated Wire: Also known as triple insulated magnet wire (TIMW), this type of Polyimide enamelled wire has three layers of insulation. It provides enhanced electrical safety and is used in applications where high-voltage insulation is required.
Each wire type mentioned above can have different specifications, such as varying diameters, temperature ratings, and insulation thicknesses, depending on the specific application requirements.
Self-bonding Wire:Self-bonding enamelled wire, also referred to as self-lubricating wire, offers a unique characteristic that sets it apart from traditional enamelled wires. It contains a bonding layer that enables the wire to stick to itself when heated, eliminating the need for additional adhesives or soldering. This type of wire is widely used in applications where coil windings need to be secured or held in place without the use of external materials. Self-bonding wire finds applications in the automotive industry, home appliances, and electromechanical devices.

Self-bonding enameled wire, also known as self-solderable wire or self-lubricating wire, is a type of magnet wire used in various electrical and electronic applications. It is designed to eliminate the need for external soldering or additional bonding agents during the winding process. There are different types of self-bonding enamelled wire, including:
Self-bonding Polyurethane (PU): This type of wire has a polyurethane insulation layer that bonds to itself when heated, forming a strong and reliable bond. It is commonly used in applications where high thermal resistance and good bonding properties are required.
Self-bonding Polyester (PE): Polyester-based self-bonding wire utilizes a polyester enamel layer that fuses together upon heating, creating a secure bond. It offers excellent mechanical strength and resistance to abrasion and chemicals.
Self-bonding Polyamideimide (PAI): Polyamideimide self-bonding wire is known for its high-temperature resistance and good bond strength. It is often used in demanding applications where the wire needs to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh operating conditions.
Self-bonding Polyesterimide (PEI): This type of wire combines the properties of polyester and polyamideimide to provide a balance of good thermal stability and bondability. It is commonly used in motors, transformers, and other high-temperature applications. See the
Class 200 Polyesterimide(PEI) Flat Enamelled Copper Wire.
Self-bonding Polyimide (PI): Polyimide self-bonding wire offers exceptional thermal and electrical properties, making it suitable for applications involving high temperatures and harsh environments. It forms a strong bond upon heating, ensuring reliable performance.
These are some of the common types of self-bonding enamelled wire available in the market. The selection of the appropriate type depends on the specific application requirements such as temperature resistance, mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and bonding properties.
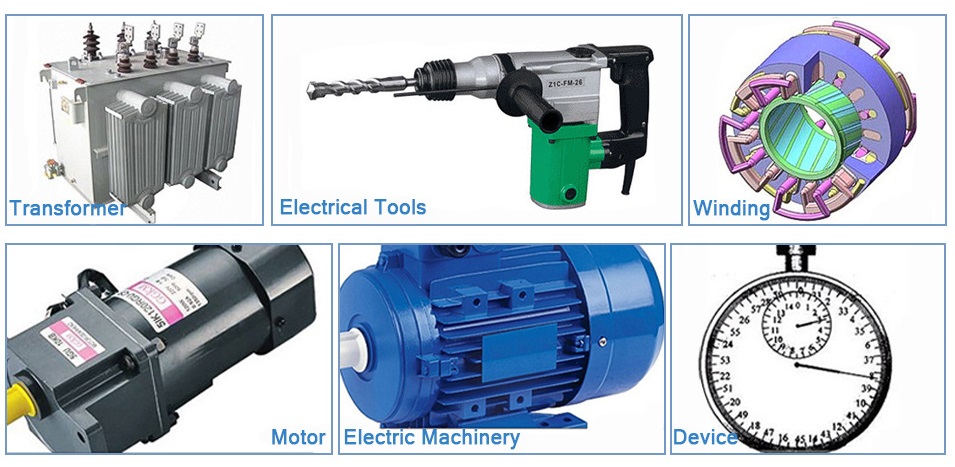 Conclusion:
Conclusion:The evolution of
enamelled wire has brought about significant improvements in electrical applications. The top five types of enamelled wire discussed above showcase a range of properties and characteristics that cater to diverse industry requirements. Whether it's polyurethane for cost-effective solutions, polyamide-imide for high-temperature environments, polyester for durability, polyimide for extreme conditions, or self-bonding wire for securing windings, these enamelled wires are revolutionizing the electrical industry in 2023. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations in enamelled wire, enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and performance of electrical devices in the years to come.


.jpg)


